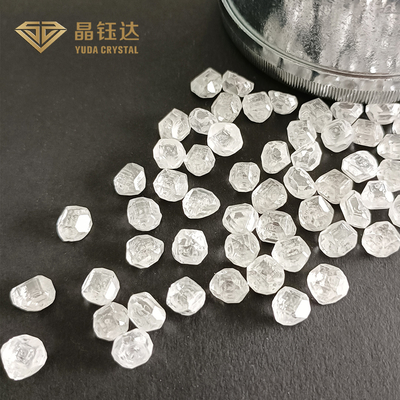
4.0ct 5.0ct DEF VVS VS Full White HPHT Lab Grown Rough Diamond For Loose Diamond
Synthetic Rough Uncut Diamonds Description
Laboratory growth of diamond, also called synthetic diamond, synthetic diamond, diamond is produced in the laboratory, and natural diamond on the chemical composition, lattice structure and physical properties are exactly the same.
High temperature and high pressure (HPHT) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is the most commonly used in synthetic diamond industry white of the two methods of growth.
Laboratory growth diamond is simulating natural diamond synthetic diamond growth environment, by using high temperature and high pressure (HTHP) and CVD (chemical vapor phase precipitation) synthesis, also called the diamond growth. Laboratory cultivation is the real diamond, physical properties, chemical composition and crystal structure of natural diamond is basically the same, all share 4C certification standards, has been IGI, GIA and other international authority certification issued by the certificate.
In recent years, the production of natural rough diamonds have been falling, but the global demand for diamonds, has increased. The imbalance between supply and demand creates opportunities for lab-made diamonds.
With the progress of human technology, scientists will have to natural diamond moved to the laboratory environment, the use of high pressure high temperature (HPHT) to simulate the diamond growth environment, with the size of the size of gravel for the growth of diamond seed.
Parameters of Synthetic Rough Uncut Diamonds
| HPHT Lab Grown Diamonds Details |
| Brand Name |
Henan Yuda Crystal |
| Name |
Rough Uncut Diamonds |
| Color |
D-F |
| Clarity |
VVS VS |
| Carat Weight |
4.0-5.0 carat |
| Cut |
Uncut |
| Technology |
HPHT |
| Diamond Shape |
Round |
| Application |
For Jewellery(necklace,ring) |
| Place Of Origin |
Zhengzhou,Henan,China |
| Delivery Time |
1 - 15 Working Days Base on Order Quantity |
| Payment Terms |
100% Payment In Advance |
| Payment Methods |
PayPal,T/T, Western Union, Bank Transfer |
| Shipping way |
DHL,SF Express, FedEx, UPS, EMS, TNT etc |
| M.O.Q |
Negotiable |
| Diamond Type |
Synthetic(lab created) |
| Location |
Zhengzhou,Henan,China |
| Fire Dispersion |
0.044(Same as Natural Diamond) |
| Brilliance Refraction Index |
2.42(Same as Natural Diamond) |
| Relative Density |
3.52(Same as Natural Diamond) |
| Chemical Composition |
Carbon(Same as Natural Diamond) |
| Moh's Hardness |
10(Same as Natural Diamond) |
Synthetic Rough Uncut Diamond Introduction
High temperature and high pressure synthesis method is also called seed catalyst method. Graphite is a low pressure stable phase, while diamond (diamond mineralogy name) is a high pressure stable phase. Graphite to diamond direct transition to high pressure and high temperature conditions, generally take 10 gpa, pressure and temperature above 3000 ℃. If involved metal catalysts (such as Fe, Ni, Mn, Co and their alloys), graphite into diamond would significantly reduce the required temperature and pressure conditions, so the high temperature and high pressure diamond synthesis method involves metal catalysts. Metal contact coal as solvent between carbon source (graphite) seeds and diamond products. Carbon source in the high temperature side, crystal seed in low temperature. As the solubility of carbon source at high temperature is greater than that at low temperature, temperature difference acts as the driving force of carbon source diffusion from high end to low end, and carbon source gradually precipitates in seed crystal and diamond crystal gradually grows up. As the driving force of the crystal growth is caused by temperature difference, so this method is also referred to as the temperature difference method.
Natural diamonds are created by nature, the result of billions of years of high temperature and pressure. Laboratory of rough diamond is produced in the laboratory, usually need a couple of weeks. The chemical difference is the same.
So how do you distinguish between rough laboratory diamond and natural diamond?
Unprocessed laboratory production of diamond and natural diamond had no obvious difference. Even professional gemologists need special equipment to identify them. By magnifying, professionals will be able to recognize in the lab, growth and production of diamond inclusions nuances.
| The Difference Between Lab Diamond And Natural Diamond |
| Properties |
Earth Mined |
Lab Created |
| Guaranteed Conflict-Free |
No |
Yes |
| Hardness (MOHS) |
10 |
10 |
| SP3 Carbon Diamond Bonds (%) |
100% |
100% |
| Internal Crystal Structure |
Face-Centered Cubic |
Face-Centered Cubic |
| Hardness Comparable |
2.42 |
2.42 |
| Relative Diversity |
3.52 |
3.52 |
| Color Diffusion |
0.044 |
0.044 |
| Color |
Various Grades |
K to D grades |
| Compressibility |
8.3*10-13 M2/N |
8.3*10-13 M2/N |
| Hardness value |
90 GPA |
90 GPA |
| Price |
$$$$$ |
$$$ |
Synthetic Rough Uncut Diamonds Details


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!