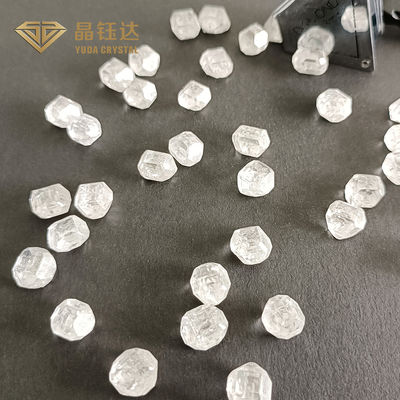
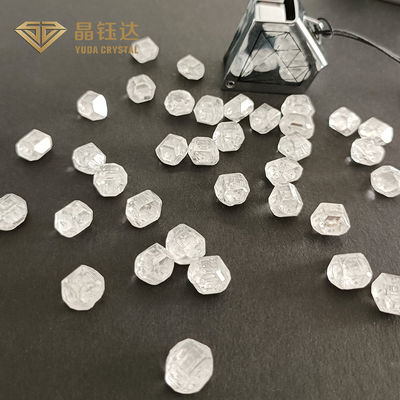
White DEF Color VVS VS SI Clarity Raw 3-4ct HPHT Lab Grown Diamonds
Lab Created Diamonds Description
It is still a short time for diamond technology to achieve a breakthrough. From the perspective of the industry life cycle, the industry is in the early stage of development.
In recent years, the output of rough natural diamonds has been declining, but the global demand for diamonds has been increasing. The imbalance between supply and demand has brought opportunities for lab created diamonds.
Lab grown diamond, also known as synthetic diamond, artificial diamond, is produced in the laboratory of diamond, and natural diamond in chemical composition, lattice structure, physical properties are exactly the same.
Lab grown diamond is artificially simulated natural diamond growth environment synthesis of diamond, HTHP method (high temperature and high pressure) and CVD method (chemical vapor precipitation method) synthesis, also known as growing diamond. Lab grown diamond is true diamond, physical properties, chemical composition and crystal structure and natural diamond are basically the same, the two share 4C certification standards, international authoritative appraisal institutions such as IGI, GIA has issued certification.
Parameters Of Lab Created Diamonds
| Product Name |
Synthetic (Lab created) diamond |
| Material |
Lab-grown |
| Color |
D-H |
| Size |
0.003PCS/CT-7CTS/PC |
| Grade |
VVS VS SI |
| Used |
Jewelry (necklace,ring) |
| Application |
For Cutting Lab Grown Loose Diamonds |
| Place Of Origin |
Zhengzhou, China |
Characteristics Of Lab Created Diamonds
| The Difference Between Lab Diamond And Natural Diamond |
| Attribute |
Lab Created Diamonds |
Natural diamond |
Distinction |
| Chemical composition |
C(carbon) |
C(carbon) |
No |
| Refractive index |
2.42 |
2.42 |
No |
| Relative density |
3.52 |
3.52 |
No |
| Dispersion |
0.044 |
0.044 |
No |
| Hardness value |
90 GPA |
90 GPA |
No |
| Thermal conductivity |
2*103 W/M/K |
2*103 W/M/K |
No |
| Thermal property |
0.8*10-6 K |
0.8*10-6 K |
No |
| Light transmittance |
DEEP UV TO FAR TR |
DEEP UV TO FAR TR |
No |
|
Resistivity
|
1016 OHM-CM
|
1016 OHM-CM
|
No
|
|
Compressibility
|
8.3*10-13 M2/N
|
8.3*10-13 M2/N
|
No
|
From a scientific point of view, cultivated diamonds are exactly the same as natural diamonds, the only difference being where they are formed.
High temperature and high pressure synthesis method is also called seed catalyst method. Graphite is the low pressure stable phase, and diamond (the mineralogical name for diamond) is the high pressure stable phase. Direct transition from graphite to diamond requires very high pressure and temperature conditions, generally requiring 10GPa, more than 3000℃ pressure and temperature. If there are metal catalysts involved (such as Fe, Ni, Mn, Co and their alloys), the temperature and pressure conditions required for graphite to become diamond will be greatly reduced, so the current high temperature and high pressure method of diamond synthesis have metal catalysts involved. The metal contact coal as solvent is located between the carbon source (one strand is graphite) and the diamond seed product. The carbon source is at the high temperature end and the seed crystal is at the low temperature end. Since the solubility of the carbon source at the high temperature end is greater than that at the low temperature end, the solubility difference generated by the temperature difference becomes the driving force for the diffusion of the carbon source from the high temperature end to the low temperature end, and the carbon source gradually precipitates at the seed crystal, and the diamond crystal gradually grows up. Since the driving force of crystal growth is caused by temperature difference, this method is also called temperature difference method.
Lab Created Diamonds Details


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!